
CSA scores: what are they and how to fix them?
-
-
December 26, 2024
-
-
In freight transportation, the term CSA stands for “Compliance, Safety, Accountability.” This is a federal program that monitors whether carriers comply with commercial vehicle requirements. CSA scores are used to assess carriers’ performance in seven key categories, known as Behavior Analysis and Safety Improvement Categories (BASICs). The lower the CSA scores, the higher the safety level. The best result is 0 out of 100 in each category.
Continue reading to learn about BASIC categories, how CSA scores are calculated, and how to improve them to work with Amazon Relay.
What Are BASIC Categories in the FMCSA System and How Are They Related to CSA Scores?
CSA scores are formed based on data from the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). Let’s consider the key terms:
FMCSA: A U.S. Department of Transportation agency that ensures compliance with safety standards.
CSA: A division of FMCSA that develops regulatory and accident prevention programs.
Safety Measurement System (SMS): A method for evaluating carrier performance based on inspection and investigation data.
BASIC Categories: Safety categories that help identify risks associated with carrier activities.
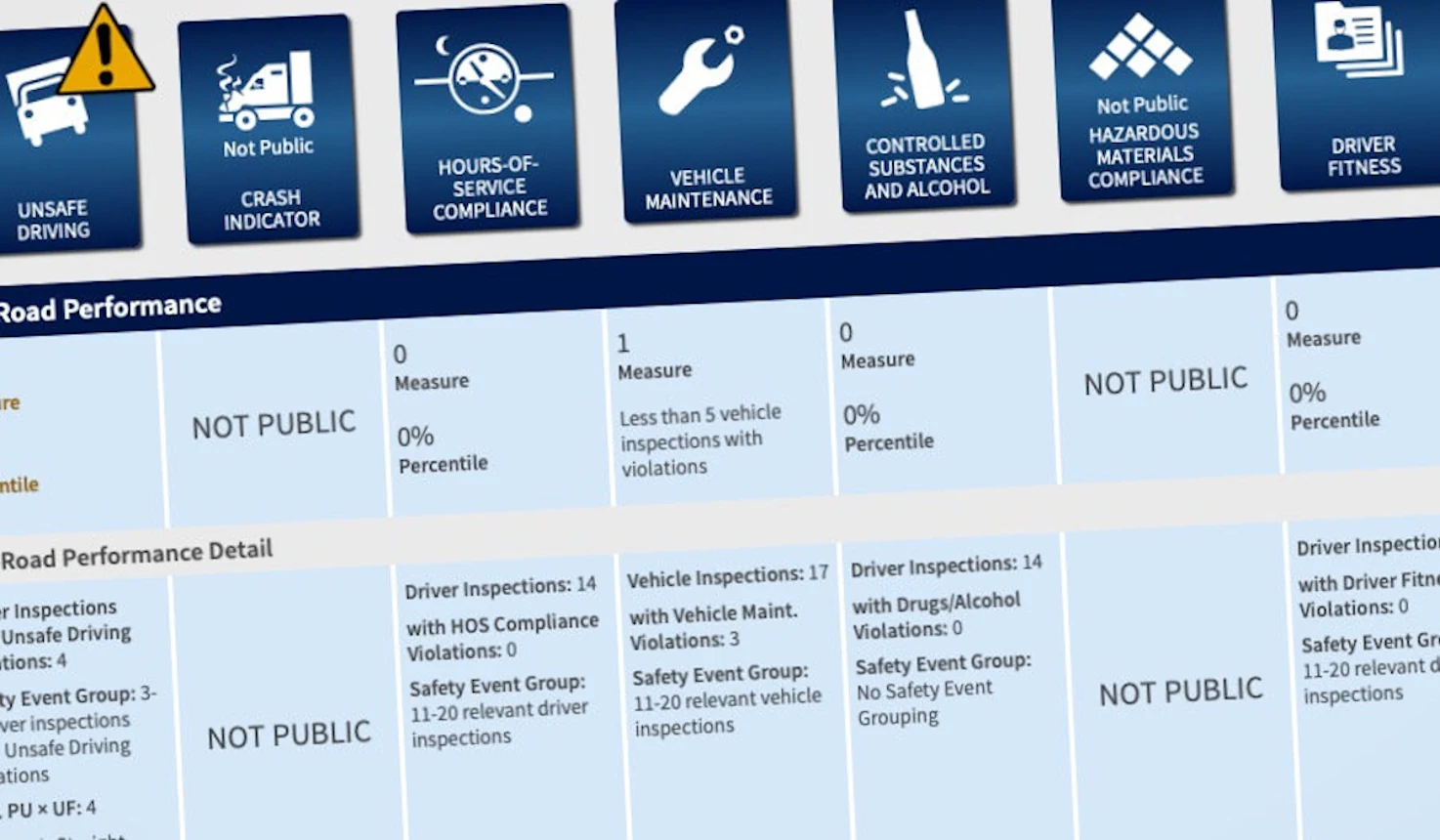
Seven BASIC Categories and Their Impact on CSA Scores
Hours of Service (HOS): Maximum working hours for drivers and related factors. Violations include driving while fatigued or ill, exceeding the 11-hour consecutive driving limit, and lacking HOS documentation.
Unsafe Driving: Dangerous behavior such as speeding, abrupt lane changes, and using phones while driving. These violations significantly worsen CSA scores.
Vehicle Maintenance: Improper vehicle upkeep, including overloading and faulty lighting. Deficiencies in this category lower carriers’ CSA scores.
Controlled Substances: Driving under the influence of alcohol or drugs, as well as violating substance testing programs.
Driver Fitness: Lack of necessary training, licenses, or medical certifications. This is one of the key factors affecting CSA scores.
Crash Indicator: Evaluation of past accidents, including severe damages requiring vehicle evacuation.
Hazardous Materials: Violations in packaging or transporting hazardous materials, which also affect CSA scores.
Why Do CSA Scores Matter?
CSA scores play a key role in the following aspects:
Public Safety: High CSA scores in any category increase the likelihood of accidents by 79%, posing risks to drivers and the public.
Operational Efficiency: Low CSA scores lead to fewer inspections and warnings from the DOT.
Reputation: Companies with low CSA scores are more attractive to major clients such as Amazon.
How Are CSA Scores Calculated?
CSA scores are updated monthly based on data from the past 24 months. Each violation adds 1 to 10 points, with more recent violations carrying greater weight. Carriers are evaluated in groups of similar size to ensure fair comparisons.
How Does Amazon Relay Use CSA Scores?
Amazon Relay uses CSA scores to assess carrier reliability. Five out of the seven BASIC categories are open for monitoring. Amazon Relay’s standards are 5% stricter than federal thresholds, making safety requirements higher.
Amazon requires the following CSA score thresholds:
Unsafe Driving: <60%
Hours of Service: <60%
Vehicle Maintenance: <75%
Controlled Substances: <75%
Driver Fitness: <75%
How to Improve CSA Scores
Protect Work Hours: Check electronic logging devices (ELDs) and train drivers to use backup documentation.
Drive Safely: Monitor speed and avoid risky road behaviors.
Maintain Equipment: Conduct regular maintenance and address issues promptly.
Document Everything: Ensure current data on driver qualifications and vehicle conditions.
Update MCS-150 Every Six Months: This helps maintain data accuracy in the system.
Motivate Drivers: Clean inspections improve CSA scores and encourage safe behavior.
Categories
- Amazon Relay 9
- Dispatch 4
- Logistic 5
Recent Posts
Understanding the U.S. Truck Dispatcher Average Salary
How Dispatchers Help Optimize Freight Costs in the USA
Related
Related Posts
-
January 8, 2025
-
January 7, 2025
-
January 7, 2025
-
December 26, 2024